High Pressure Hose Testing Equipment: An Essential Tool of Oilfield Equipment
Oilfield equipment operates in demanding environments, often under extreme pressure. High-pressure hoses are critical components that transfer fluids for various functions, including drilling, well completion, and hydraulic fracturing. These hoses are subjected to significant wear and tear, and their integrity directly affects the safety and efficiency of oilfield operations.
Regular testing with high-pressure hose testing equipment is essential to ensure the hoses can withstand the pressures they are designed for. This proactive approach helps prevent potential accidents, costly downtime, and environmental hazards.
What is High-Pressure Hose Testing Equipment?
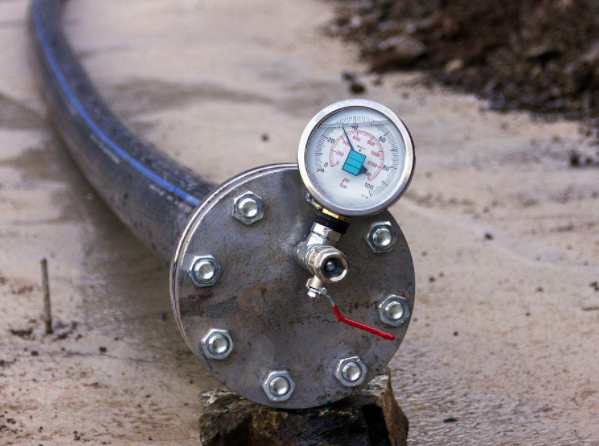
High-pressure hose testing equipment is a specialized tool used to verify the structural integrity of high-pressure hoses employed in oilfield applications. These testers generate a controlled amount of fluid pressure within the hose, exceeding its normal operating pressure. By monitoring the hose for leaks, pressure loss, or bursts, technicians can assess its fitness for service.
There are several types of high-pressure hose testing equipment commonly used in the oilfield industry:
- Air-driven hydrostatic test pumps: These pumps utilize compressed air to create hydraulic pressure within the hose. They are typically portable and well-suited for testing hydraulic hoses in various field settings.
- Gas boosters: These systems employ compressed gas, such as nitrogen, to generate the necessary pressure for testing. Gas boosters are often trailer-mounted and used for high-pressure applications.
- Automated testing equipment: These advanced testers offer a high degree of control and data recording. They can automatically regulate pressure, monitor for leaks, and record test data for future reference. Some models even include features like remote monitoring capabilities.
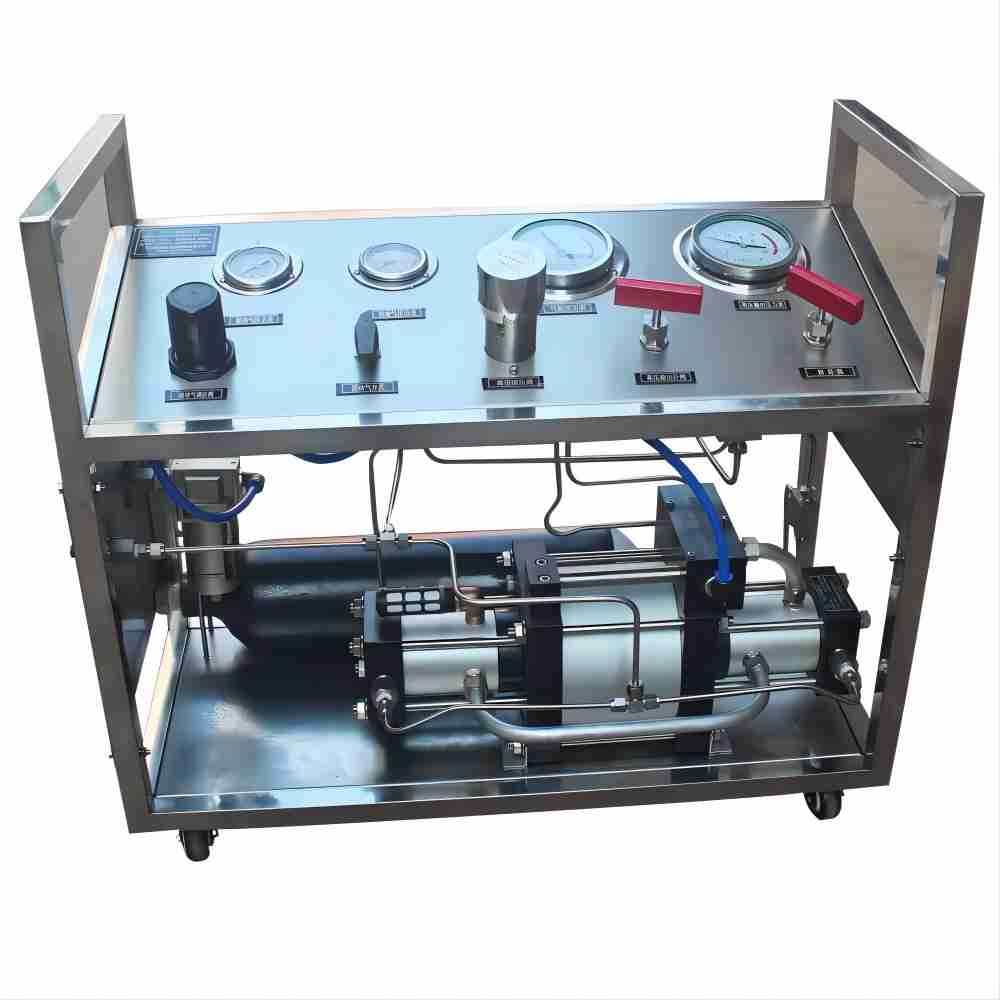

How Does High-Pressure Hose Testing Work?
The process of high-pressure hose testing in oilfield environments typically follows these steps:
- Pre-Test Inspection: This initial stage involves a meticulous examination of the hose to identify any potential weaknesses. Technicians visually inspect the entire length of the hose for cuts, abrasions, signs of wear and tear, or any other visible damage. Special attention is paid to the hose’s outer layer, as well as the couplings and connectors at each end. These connections are checked to ensure they are securely fastened and free of any defects.
- Equipment Connection: Once the hose is deemed ready for testing, the chosen testing equipment is connected to it. This process involves using appropriate adapters and fittings specifically designed for the hose size and type. The technicians ensure a secure and leak-proof connection between the testing equipment and the hose to prevent any pressure loss during the test.
- Gradual Pressurization: With the connection established, the testing equipment is activated. The pressure within the hose is then steadily increased in a controlled manner. This pressurization process is gradual to allow for any weaknesses in the hose to become apparent before reaching the maximum test pressure.
- Reaching and Holding Test Pressure: The pressurization continues until the hose reaches a designated test pressure. This target pressure is always higher than the hose’s normal operating pressure. The specific safety factor by which the test pressure exceeds the operating pressure is predetermined based on relevant regulations and industry standards. Once the test pressure is achieved, it is held constant for a specific duration to assess the hose’s ability to withstand that level of pressure for a sustained period.
- Rigorous Leak Detection: Throughout the entire pressurization process, the hose is continuously monitored for leaks. Technicians perform a visual inspection, meticulously examining the hose for any signs of fluid escaping. A common technique involves applying a soapy water solution to the hose exterior. If a leak exists, bubbles will form at the leak point as the pressurized fluid pushes through the soapy water. In some cases, more sophisticated electronic leak detection equipment may also be used for added accuracy.
- Controlled Pressure Release: After the test duration has elapsed, the pressure within the hose needs to be safely released. This is achieved using a controlled bleed-off valve that gradually reduces the pressure in a controlled manner. This prevents any sudden pressure drops that could potentially damage the hose or pose a safety risk to personnel nearby.

Importance of High-Pressure Hose Testing in Oilfield Operations
The unforgiving environment of oilfields presents significant risks associated with high-pressure hose failure. A sudden burst in a hose can cause the following serious consequences:
- Safety Threats: High-pressure fluid releases pose a direct safety hazard to personnel working near the equipment. These pressurized fluids can strike workers with significant force, causing serious injuries.
- Environmental Damage: Hoses often contain hazardous fluids like oil or contaminants. If a hose ruptures, these fluids can leak or spill onto the ground, contaminating soil and water resources. The potential environmental impact of such a spill can be severe and require extensive cleanup efforts.
Regular high-pressure hose testing plays a proactive role in mitigating these risks by identifying weak or damaged hoses before they fail. Here’s how this preventative measure benefits oilfield operations:
- Enhanced Safety: Perhaps the most critical benefit is the significant improvement in safety for personnel working on oil rigs. By proactively identifying weak or damaged hoses before they rupture, testing helps prevent accidents and injuries caused by pressurized fluid releases. These releases can be forceful and pose a serious threat to workers nearby.
- Reduced Downtime: Unexpected hose failure can bring oilfield operations to a screeching halt. The time required for repairs and replacements translates to significant downtime and lost productivity. Regular testing ensures hoses remain operational, minimizing downtime and keeping oilfield activities running smoothly.
- Optimized Equipment Performance: Damaged hoses can have a detrimental impact on equipment performance. They may restrict fluid flow, leading to inefficiencies in the system. Pressure drops caused by damaged hoses can also hinder the optimal operation of equipment. Regular testing helps identify such issues and allows for timely repairs or replacements, ensuring equipment performs at its peak capacity.
- Environmental Protection: Hoses often contain oil or other hazardous fluids. A burst hose can lead to spills and leaks, posing a significant threat to the environment. Regular testing plays a vital role in preventing such environmental hazards by identifying weak hoses before they fail.

Selecting the Right High-Pressure Hose Testing Equipment
Choosing the appropriate high-pressure hose testing equipment for oilfield applications requires careful consideration of several factors:
- Pressure Requirements: The tester’s maximum pressure output should exceed the rated working pressure of the hoses being tested by a specific safety margin. Typical safety factors range from 1.25 to 1.5 times the working pressure.
- Hose Size and Compatibility: The testing equipment must be compatible with the size and type of hoses used in the operation. This includes factors like hose diameter, thread connections, and the type of fluid being conveyed.
- Portability vs. Skid-Mounted Units: Portable testers offer greater flexibility for field use, while skid-mounted units are often more powerful and suitable for high-volume testing applications.
- Automated Features: While not always essential, automated testing equipment can provide valuable benefits like improved data recording, automatic pressure control, and remote monitoring capabilities. This data can be used for trend analysis, preventative maintenance scheduling, and ensuring compliance with industry regulations.
Regulations and Standards
The oil and gas industry adheres to various regulations and standards for ensuring the safety and integrity of equipment used in exploration and production activities. These standards often include specific requirements for high-pressure hose testing.
A prominent example is the American Petroleum Institute (API) which publishes a range of standards for oilfield equipment and procedures. API standards relevant to high-pressure hose testing equipment include:
- API 16C: This standard specifies requirements for hoses used in hydraulic fracturing and well servicing operations. It also outlines testing procedures and pressure ratings for these hoses.
- API 5C: This standard covers specifications for pipes and tubular goods used in oilfield applications. It provides guidance on pressure testing procedures for pipelines and associated components.
Following these established regulations and standards ensures that high-pressure hose testing is conducted using reliable and safe practices.

Conclusion
High-pressure hose testing equipment plays a critical role in maintaining the safety, efficiency, and environmental responsibility of oilfield operations. By regularly subjecting hoses to rigorous testing procedures, oilfield companies can identify and address potential issues before they escalate into costly accidents or environmental hazards. As technology advances, high-pressure hose testing equipment is expected to become even more sophisticated, with features like further automation, remote monitoring capabilities, and more user-friendly interfaces. This continuous improvement will contribute to even greater safety, efficiency, and reliability in the demanding world of oilfield operations.






